Friday, 10 September 2021
Thursday, 9 September 2021
Most Frequently Used UNIX / Linux Commands
vim :Vim is a text editor. The most simple commands allow you to open and close documents as well as saving them
Install Vim on Ubuntu/Debian:
If you're using Ubuntu or Debian use apt-get to install Vim:
sudo apt-get install vimInstall Vim on CentOS/Fedora:
If you're using CentOS or Fedora, use yum to install Vim:
sudo yum install vimpwd Print working directory command in Linux
 |
ifconfig : The ifconfig command will give you the list of all the network interfaces along with the IP addresses, MAC addresses and other information about the interface.
if the tool ifconfig is not installed then you can install using the below commons
 |
sudo: Super User ( sudo apt-get update ) | Command to escalate privileges in Linux
grep 'two' /~Download/sample1.doc
Wednesday, 8 September 2021
Saturday, 4 September 2021
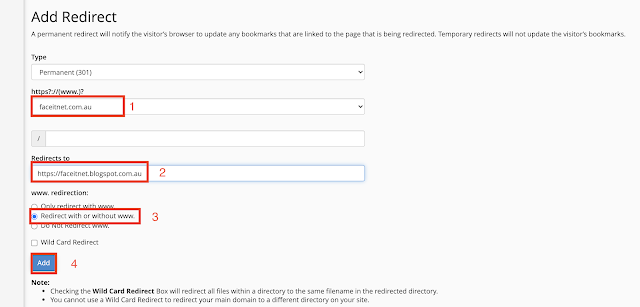
How to redirect your old website to new URL ( URL /Website Redirection)
How to redirect the website to a new domain name? (URL Redirection/Web Redirection)
- 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that shows the new URL and carries over Google PageRank.
- 302 redirects are temporary and display the new URL.
- URL frames are redirects that display a frame from the website you’re redirecting to.
- Meta refresh is a redirect that happens in the browser. It shows a specific message and a countdown timer before redirecting to a different page.
Friday, 3 September 2021
Self-Signed SSL certificate on exchange server 2019
Create Exchange Server 2019 SSL Certificate Request
Wednesday, 1 September 2021
TOP 20 UNTIMATE WINDOWS CMD COMMANDS
Subscribe to " FACEITNET " Youtube channel for more interesting videos
The Microsoft Windows command prompt is a great feature and core the Windows operating system. There are some CMD commands that are very useful and easy to use by standard users see the Windows information.
Lets see few of the commands
1) Ping :
Verifies IP-level connectivity to another TCP/IP computer by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo Request messages. The receipt of corresponding echo Reply messages are displayed, along with round-trip times.
 |
| ping with successful response |
 |
| ping /a 192.168.20.11 |
2) TRACERT: Trace Route
This diagnostic tool determines the path taken to a destination by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo Request or ICMPv6 messages to the destination with incrementally increasing time to live (TTL) field values. Each router along the path is required to decrement the TTL in an IP packet by at least 1 before forwarding it.
 |
| Tracert google.com |
 |
| Prevent the resolution of each IP address to its name |
3) tskill:
Ends a process running in a session on a Remote Desktop Session Host server.

4) ipconfig /all:
Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
5) gpupdate :
Updates Group Policy settings.
gpupdate /force
gpupdate /force
gpresult /R
6) ipconfig /flushdns
To flush the DNS resolver cache when troubleshooting DNS name resolution problems, type.
7) nslookup:
Displays information that you can use to diagnose Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure.
8) FC:
Compares two files or sets of files and displays the differences between them.
9) NETSTAT: Network Statistics
Displays active TCP connections, ports on which the computer is listening, Ethernet statistics, the IP routing table, IPv4 statistics (for the IP, ICMP, TCP, and UDP protocols), and IPv6 statistics (for the IPv6, ICMPv6, TCP over IPv6, and UDP over IPv6 protocols).
10) SHUTDOWN: Turn Off Computer
11) SYSTEMINFO: System Information
Displays detailed configuration information about a computer and its operating system, including operating system configuration, security information, product ID, and hardware properties (such as RAM, disk space, and network cards).
12) Taskkill
Ends one or more tasks or processes. Processes can be ended by process ID or image name.
13) Chkdsk
14) cls
15) Hostname
Displays the host name portion of the full computer name of the computer.
16) getmac
Returns the media access control (MAC) address and list of network protocols associated with each address for all network cards in each computer, either locally or across a network.
17) arp:
Displays and modifies entries in the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache. The ARP cache contains one or more tables that are used to store IP addresses and their resolved Ethernet or Token Ring physical addresses
To display the arp cache table for the interface that is assigned the IP address 192.168.20.15,
arp /a
18) Mkdir
19) quser:
Displays information about user sessions on a Remote Desktop Session Host server.
20) net user
Adds or modifies user accounts, or displays user account information
Net User is a command line tool that allows system administrators to manage user accounts on Windows PCs
net user Saththiyan
-
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"...
-
Subscribe to " FACEITNET " Youtube channel for more interesting videos FaceITNet Youtube Channel IDS using SNORT Install...
-
Subscribe to " FACEITNET " Youtube channel for more interesting videos FaceITNet Youtube Channel Most of us have used Cisco Pa...