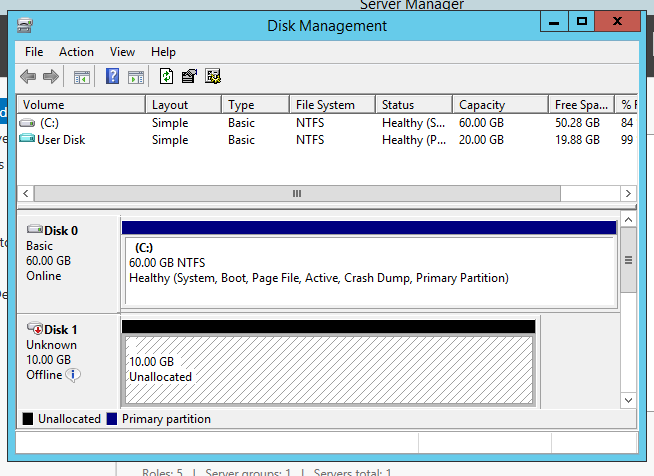
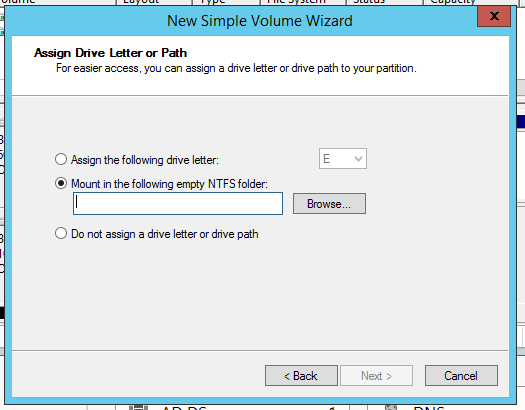
Here i am going to explain few useful linux commands which may be really handy when you need to troubleshoot sometimes.
First of all linux has every configuration file as text file, so its really easy to modify as you like,
Firstly we will have a look on Users, Groups , Permissions,
Here we go first with Users,
In linux its really easy to create users and edit the user, Its all text file, Just like adding words in a word file.
To create user :
Remember we need to use always SUDO its like "super user do the work"
sudo adduser
to delete a user
sudo userdel
and this user details are stored in a file call Passwd which is in /etc/passwd location
using a text editor we can open the file and have a look.
sodo vi /etc/passwd this is where you can see all the created users and the system default users,
so you may think then where is the password to this user, you can see when you add a user the system the system will ask you to enter all the password , firstname, lastname, so its quite easy to create a user and set a password,
But what if you want to change the password for a user which was created earlier?
so issue the following command and set the new password
sudo passwd then enter, now you can see the system will ask you to enter the new password.
So the creation of user and changing the password is very simple,
Now as in windows, linux too has groups for each users. we will have a look how we can create modify a group in linux.
To create a group
sudo groupadd
to delete a group
sudo groupdel
now we will see how we can add a user which we have created just above to a group
so to add the user to a group
sudo adduser
to delete user from a group
sudo deluser remember the different between userdel and deluser, to delete user its
userdel and to delete user form a group its
deluser
again as like the users , group details also saved as text file in the /etc/group location, with the help of vim or vi editor you can modify the groups and add users in this text file also. To add multiple users to a group just need to put comma (,) and add the user names on the right site that is all users added to group in text mode.
Now we will have a look on Permission, as you all know linux is more secure and really concern on its security on the files and directories so an administrator can change the security permission with the command call chmod.
basically linux has boolian number system to mention the permission
4- read
2-write
1-execute
so if a file has permission 777 means, in this three 7 each one of this for a special reason ,
the first digit is to specify the permission of this file owner , 2nd one to specify the permission of this file owner group 3rd one is to mention the permission of every one else in this world,
So 7 means 4+2+1 which says the owner has permission to read , write and execute this file or directory,
the execute is a special case in linux where we may have some files to run like exe files in windows. so with out the execute permission we cannot run that file. So make sure if you have any files to execute you must give the permission.
consider a website you are running, so in that case you may need to do read and write work to htdocs directory.
so the user is you should have full permission , then give 7 to user, then the group of your user give 7 so every one in your group can have full permission, but what if you give full permission to everyone else? then ppl can do what ever they want and delete your files but remember some php files do need to execute so we ll give permission to read and execute and take the write permission out from others
so we will set the permission to 775 to a website directory. I hope you will get an idea about the permission now.
Alright so we have seen user, group, and permission but there is a big doubt while doing this all, what if i want to search a file in linux , how do i search?
linux has easy way to search files with different options,
sudo find -iname , what is this iname means , its omit the case sensitive file name, So if you are not sure the file name has a capital or small letter dont worry just put -iname it will search and give you all the files such as Home,home,homE all are same in this case.
also if you are not sure the full file name you can use the * to search files with known characters such as wp-config.* this will display all the files with wp-config.
alright so we have come to a point where we got few idea about linux.
Now we will look the basic Networking stuffs in linux, this is very very basic only,
as in windows linux to has commands to see the ip address details but we have small change here , Windows use ipconfig but linux uses it as ifconfig.
and in windows we can release and renew the DHCP ip but then on linux how do you do that?
simple
sudo dhclient this command will renew your IP from your DHCP server. remember we have to restart always if we do changes to a service so linux service for networking has to be restarted to active this changes , how do you restart the service?
sodu /etc/init.d/networking restart. this will restart the networking service , further you can use start, stop instead of restart.
as i explained for users and group linux save the networking files details under the folowing location
using the vi editor we can open and see the configurations.
sudo vi /etc/networking/interfaces this is where we have the IP configuration details for linux.
if you want the linux machine to get IP from DHCP just modify the file as like this
iface eth0 inet DHCP
if you want to assign IP manually then
iface eth0 inet static then add the address details of your IP addres
Address
netmask
Network
Broadcast
gateway
DNS
So as we talk the DNS what is the file has the DNS details and resolve informations as like host file in windows
open the file
sudo vi /etc/resolve.conf and change what ever the details you need to add,
if we talk DNS then we need to talk about the hostname as well so to see the hostname
sudo /etc/hostname will display the hostname and to change this
sudo /etc/hostname
hope the details are use full and i ll keep posting more in future, on UFW firewall TAR and BACKUP.