How to configure Windows Event Log Forwarding
In a small and medium level business your budged will not allow you to buy and run a dedicated event reader. Since these days business depend on multiple servers and services its not easy for a system administrator to read all the events separately on the servers.
For this kind of situations Microsoft introduced Event Forwarding. Event Forwarding allows administrators to get events from remote computers, also called source computers or forwarding computers and store them on a central server; the collector computer.
Events can be transferred from the forwarding computers to the collector computer in one of two ways:
Collector initiated – Using this method, the collector will contact the source computers (clients) and ask them for any events they might have. The minimum operating system level required on the source computers is Windows XP SP2 with minimum Windows Remote Management 1.1 installed.
Source initiated – By using this method the clients or forwarders transfer events to the collector as required. Systems like Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008/R2 and Windows Server 2012/R2 can be Event Collectors, but this feature is not supported for down-level operating systems. Even tough there are no limitations when a client operating system is used as an Event Collector, a server platform is recommended since will scale much better in high volume scenarios.
(http://www.vkernel.ro/blog/how-to-configure-windows-event-log-forwarding)
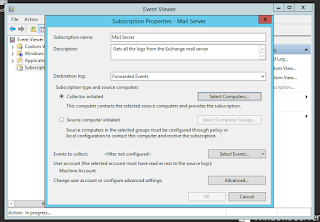
Configuring event forwarding collector initiated subscriptions ( Step by Steps )
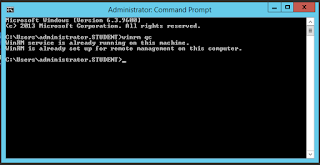
Let’s start by enabling WinRM on the Event Forwarders machines (the clients); and we have two choices here: we either use Group Policy to enable WinRM or we do it manually by issuing the bellow command on a client by client basis:
In my Example i have used WIN2K12MAIL as client.
winrm qc
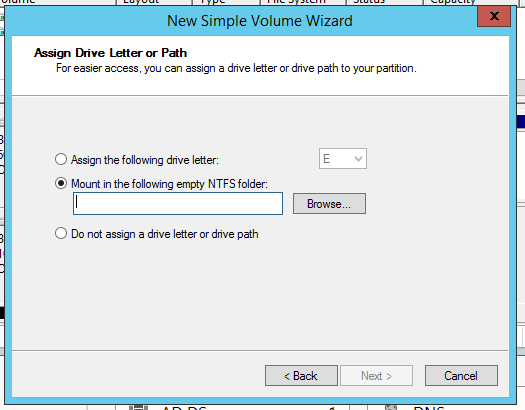
If your clients are running Windows server 2012 and above, WinRM it’s enabled by default on them, but just to be sure, you can check the configuration using the bellow command line:
winrm get winrm/configNow that WinRM it’s enabled on all our Event Forwarder computersNow we have to configure Collector computer rights to read the logs from this computersWe can use the Event Collector computer account itself for authentication, or we can create a user account in Active Directory and use thatI have created an account called eventforwarder and added this to the default Event Log Readers Group.Creating new user eventforwarderAdding eventforwarder to default Event Log Readers Group
wecutil qcContinue and if its Success let’s move forward and create a subscription on the collector computer which “tells” this one for what type of event logs to look for and collect from the forwarder computersGO to Event Viewer and Right click on Subscription, Create new SubscriptionNow we have to select what events we wants to receive, so click on Select Events buttonThe last step to make this work is to configure the account used by the collector machine to connect to clients. We already added this account to the local Event Log Readers group on every forwarder, so we should not have access problems.Click the Specific User button, provide the account and credentials and click OK, then move down to the Event Delivery Optimization section where we have three options:Normal This option ensures reliable delivery of events and does not attempt to conserve bandwidth.It gets the events every 15 minutes by using a pull delivery mode.Minimize Bandwidth – This option ensures that the use of network bandwidth for event delivery is strictly controlled.It uses push delivery mode and it uses a heartbeat interval of 6 hours.Minimize Latency – This option ensures that events are delivered with minimal delay. It is an appropriate choice if you are collecting alerts or critical events. It uses push delivery mode every of 30 seconds.I have done this way but it didn't work, Access Denied , So i have changed the User access toAdministrator and it worked ..Didn't workThe one workedNow i can see the Forwarder is been addedAfter ~10 minutes or less, depending on how you configured the Event Delivery Optimization options, logs should start coming inThat is all. Its working ...